Tox in The Land: Toxicologic Causes of Acute Liver Failure
Definitions
Acute liver failure (ALF)
“Rapid deterioration of liver function”
INR > 1.5
Encephalopathy
King’s College Criteria for transplant:
Arterial pH < 7.30
INR > 6.5
Creatinine > 3.4mg/dL
Grade III or IV hepatic encephalopathy
Differential
What is on your differential for acute liver failure?
What labs should be ordered?
Do you always get an acetaminophen level...spoiler alert...you should.
Acetaminophen
#1 cause of acute liver failure in the United States
Single toxic ingestion >7.5g
Limited ability to clear NAPQI in large overdoses
4 clinical phases:
Asymptomatic/mild symptoms
RUQ pain/worsening symptoms
Hepatic phase
Recovery
Start NAC within 8-10 hours
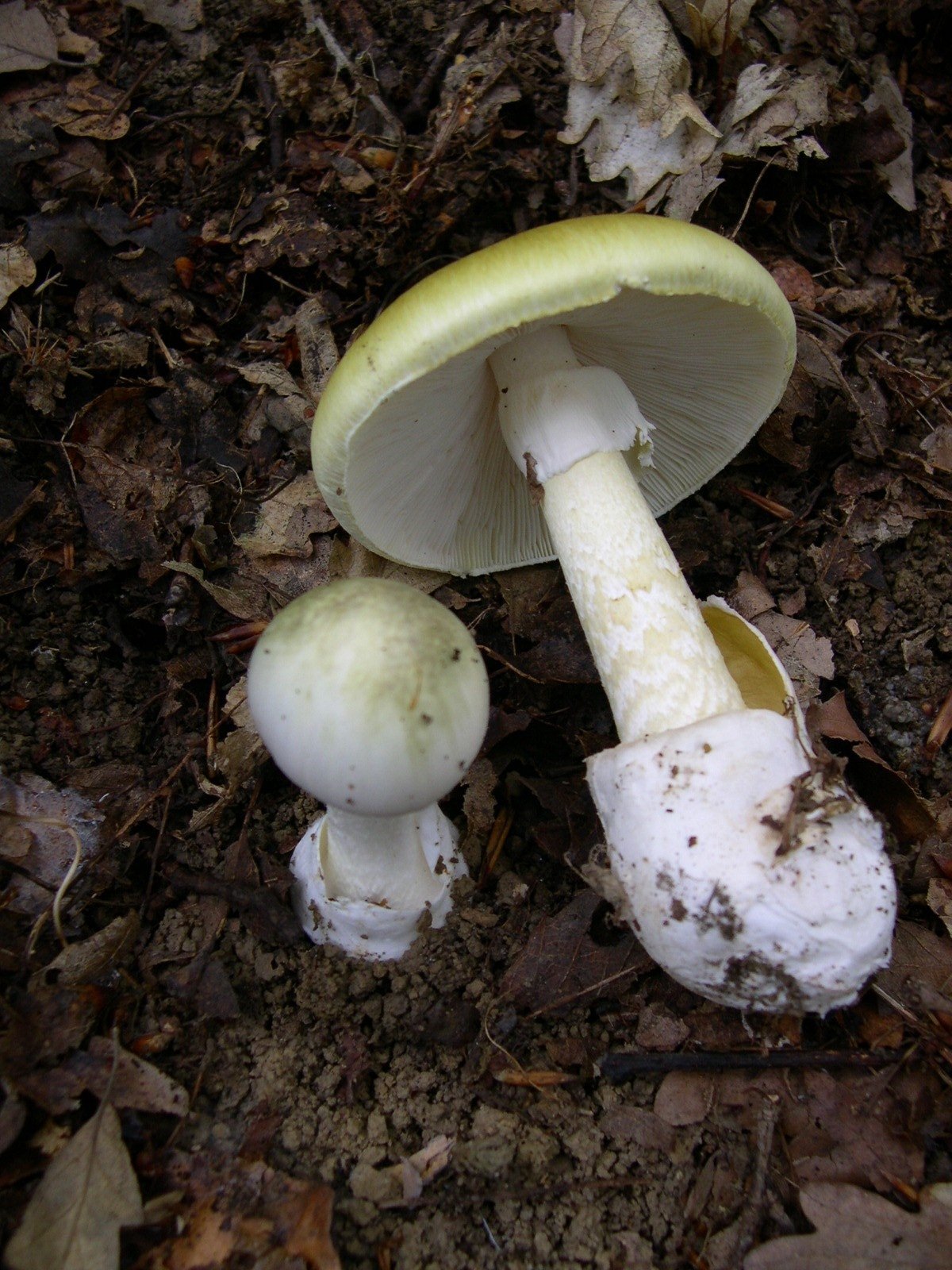
What about mushroom lovers and foragers out there? Are all mushrooms created equal? When in doubt, just get them from the grocery store
α-amanitin
Amanita phalloides (“death cap”)
Most potent amatoxin currently classified
RNA polymerase II inhibitor
Detectable in urine, serum, emesis
Clinical presentation:
Gastrointestinal symptoms in first 24 hours
Latent phase
Clinical hepatic +/- renal failure
J WS, et al. 2014 [5]
Treatment
Supportive
NAC
Transplant
Silibinin?
Perchloroethylene (PERC)
Chlorinated solvent used in dry cleaning and degreasing industries
Known carcinogen, hepatotoxicity in animal studies
Colorless, sweet odor
High VD
Presents clinically after oral ingestion or inhalation with AMS, hepatic and renal failure
Plasmapharesis
Copper
Essential trace mineral
RDA 1.5 mg/day
Single toxic ingestion >1-10g
Agricultural/marine fungicide
Mechanism:
Lipid peroxidation
Free radical production
Decreased cytochrome c oxidase activity
Case reports of acute liver failure developing within hours
Clinical presentation:
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy within 24-72hrs
Multi-organ involvement
High mortality rate
ALF indicates poor prognosis
Chloroform
Colorless, sweet-smelling liquid
Converted to phosgene gas in air
Original medical use as anesthetic
Presents with depressed CNS status, hepatotoxicity
Detectable in serum
Potential benefit of NAC
Etc. Etc.
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
Green tea extract
Halothane
Pennyroyal
Phosphorous
Black cohosh
Isoniazid
Take Home Points
Acetaminophen responsible for > 1/3 cases in the US
High index of suspicion
Use your social history!
When in doubt, NAC
POST BY: DR. EMILY CRAFT (PGY3)
FACULTY EDITING BY: DR. LAUREN PORTER (MEDICAL TOXICOLOGIST)